2023. 1. 20. 14:08ㆍBackEnd(Java)/Spring Boot
✅ 아래 내용들에 대해서 알아보자
- 이벤트란 무엇일까?
- 스프링 이벤트 처리 방법
- 예제 코드 & 실습
- 이벤트 발송 프로세스
이벤트란?
컴퓨팅에서 이벤트(event)란 프로그램에 의해 감지되고 처리될 수 있는 동작이나 사건을 의미합니다.
예를 들어 사용자가 키보드의 키를 누르는 행위, 사용자가 화면의 버튼을 누르는 것 등의 행위들을 의미한다.
분산 시스템 간에 이벤트를 생성, 발행(publish)하고 발행된 이벤트를 필요로하는 수신자에게 전달하여 수신자가 이벤트를 처리하는 형태의 시스템 아키텍처를 Event-driven-architecture(EDA)라고 한다.
스프링 이벤트 처리 방법
스프링의 Application context는 BeanFactory 기능 말고 여러가지 기능들을 제공하는데 그중 ApplicationEventPublisher 인터페이스를 extends 하고 있다.
ApplicationEventPublisher는 Event를 받아,Listner들에게 Event를 publish(발송) 해준다.
간단히 예제 코드를 보자


엔티티
@Getter
@ToString
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public static User of(String name, int age) {
User user = new User();
user.name=name;
user.age=age;
return user;
}
}
이벤트 등록
Application를 상속받아야 Event로 사용 가능
(스프링 4.2버전 이후로 위 이벤트 클래스를 상속받지 않아도 이벤트가 등록이 되기 때문에 상속받지 않아도 됨)
@ToString
@Getter
public class UserEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private final User user;
public UserEvent(Object source) {
super(source);
this.user = (User) source;
}
}
publisher 코드
ApplicationContext를 주입받아 사용해도 괜찮지만, 명시적으로 ApplicationEventPublisher를 주입받아 사용한다.
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserService {
private final ApplicationEventPublisher publisher;
public void publishEvent(User user){
publisher.publishEvent(new UserEvent(user));
}
}
Listener 등록
@Slf4j
@Component
public class UserEventListner2 {
@EventListener
// @TransactionalEventListener(phase = TransactionPhase.AFTER_ROLLBACK)
public void eventHandle(final UserEvent event){
log.info("UserEventListner2 이벤트 수신 완료");
log.info("--------------");
log.info("event = {}",event);
log.info("--------------");
log.info("UserEventListner2 이벤트 처리 완료");
}
}
테스트코드
@SpringBootTest
class UserServiceTest {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@DisplayName("이벤트 처리 테스트")
@Test
public void eventPublish() throws Exception {
//given
User user = User.of("aaa", 29);
//when
userService.publishEvent(user);
//then
}
}
그렇다면 Spring은 어떻게 이벤트를 발생시키고, 수신할 수 있을까..? 🧐🧐
내부속으로 들어가 보자!
이벤트 발송 프로세스
AbstractApplicationContext 클래스에 publishEvent 구현체가 존재한다.
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}
발송 순서
- publishEvent(…) 코드를 보면 getApplicationEventMulticaster()로 얻어온 ApplicationEventMulticaster에게 Event 처리를 위임한다
- getApplicationEventMulticaster(). multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType) 메서드를 실행해서 이벤트를 처리하는데 해당 코드를 보면 getApplicationListeners() 메서드를 통해 리스너들을 가져와 ApplicationEventMulticaster클래스의 구현체인 SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 클래스의 multicastEvent()를 호출한다
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.class
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
3. getTaskExecutor()를 통해 executor 널 체크 후 실행한다.(기본 null임) 그리고 invokeListener() 메서드를 통해 리스너들에게
이벤트를 발송함과정
과정 도식화
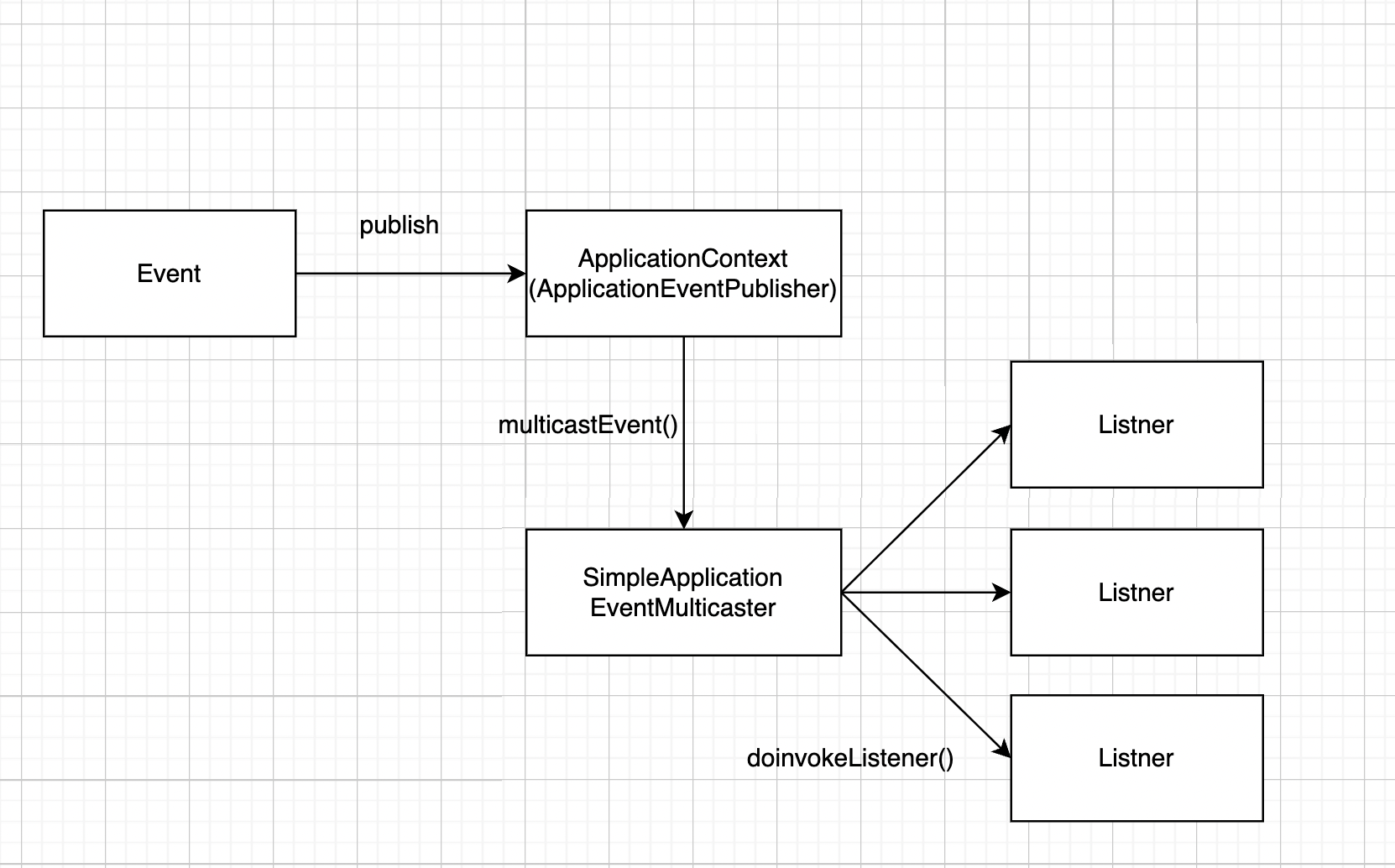
여기 까지는 등록된 리스너들에게 이벤트를 발송하는 과정이다.
그렇다면 리스너들은 어디에 등록되어 있고, 어떤 방식으로 등록되는지 알아보자
리스너 등록 과정
참고자료
'BackEnd(Java) > Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| @Meta Annotation에 대해서 알아보자 (0) | 2023.02.24 |
|---|---|
| 스프링 IoC/DI 찍먹 (0) | 2023.02.24 |
| Doesn't say anything about org.gradle.plugin.api-version (required '7.6') (0) | 2023.01.03 |
| @Async에 대한 이해 (0) | 2022.11.21 |
| javax.Transactional vs spring.Transactional (0) | 2022.09.17 |